 PDF(23699 KB)
PDF(23699 KB)


 PDF(23699 KB)
PDF(23699 KB)
 PDF(23699 KB)
PDF(23699 KB)
变截面弹体斜侵彻两层间隔钢靶弹道特性
Study on Ballistic Characteristics of Variable Cross-section Projectile Obliquely Penetrating Two-layer Spacer Steel Target

为研究变截面弹体斜侵彻两层间隔钢靶时结构特征对弹道特性的影响规律,开展椭圆等截面、椭圆变截面弹体在1020m/s初速、5°着角条件下斜侵彻两层间隔钢靶实验,结合数值模拟对比圆等截面、椭圆等截面、圆变截面和椭圆变截面弹体在斜侵彻钢靶过程中的弹道轨迹、速度、偏转角、纵向位移和纵向加速度的变化情况,揭示变截面弹体结构特征影响弹道稳定性的物理机制。研究结果表明:当弹体初始撞击速度较大、弹肩处横截面面积一致及变截面角度在0°~2.5°范围内时,不同横截面形状和变截面角度弹体在斜侵彻两层间隔钢靶过程中的速度变化差异很小;对于变截面弹体,可以通过改变变截面结构特征找到一个使得弹体贯穿首层靶板后纵向位移基本为零的临界变截面角度;不同横截面形状的变截面弹体受变截面角度对贯穿钢靶后纵向运动、姿态偏转的敏感程度不同,横截面形状的长短轴之比越大,变截面角度对偏转角速度的影响越大;变截面角度会影响弹体穿靶过程中的受力方向,可能导致弹体受力出现反转现象。相关研究对变截面弹体结构特征参数的优化、变截面弹体斜侵彻两层间隔钢靶弹道特性预测具有较好的指导价值。
The influence of the structural characteristics of variable cross-section projectile on the ballistic characteristics during obliquely penetrating the two-layer spaced steel targets is studied.The elliptical and variable cross-section projectiles obliquely penetrate a two-layer spaced steel target at an initial velocity of 1020m/s and an impact angle of 5° in the experiments.The trajectories,velocities,deflection angles,longitudinal displacements and longitudinal accelerations of circular and elliptical equal cross-section projectiles,and circular-and elliptical-variable cross-section projectiles during obliquely penetrating the steel target are compared by numerical simulations,and the physical mechanism of which the structural characteristics of variable cross-sectional projectile affect the stability of its trajectory is revealed.The results indicate that,when the initial impact velocity of projectile is high,the cross-sectional area at the shoulder of projectile remains consistent,and the variable cross-sectional angle is within the range of 0° to 2.5°,the velocity variations of projectiles with different cross-sectional shapes and variable cross-sectional angles during obliquely penetrating two-layer spaced steel targets are very small.For the variable cross-section projectile,a critical variable cross-section angle can be found by changing the structural characteristics of variable cross-section projectile,which makes the longitudinal displacement of the projectile penetrating the first-layer target plate basically zero.Different cross-sectional shapes of variable cross-sectional projectiles have different sensitivities to longitudinal motion and attitude deflection after penetrating the steel target at variable cross-sectional angles.The greater the ratio of long axis to minor axis of cross-sectional shape is,the greater the influence of variable cross-sectional angle on the deflection angular velocity is.Variable cross-section angle has an affect the force direction of the projectile during the process of penetrating the target,which may lead to the reversal of force on the projectile.The relevant studies have good guiding value for the optimization of structural characteristic parameters of variable cross-sectional projectile and the prediction of trajectory characteristics of variable cross-sectional projectiles during obliquely penetrating two-layer spaced steel targets.
变截面弹体 / 结构特征 / 弹道特性 / 斜侵彻 / 间隔钢靶 {{custom_keyword}} /
variable cross-section projectile / structural characteristics / ballistic characteristics / oblique penetration / spaced steel target {{custom_keyword}} /
表1 3类实验弹体结构参数Table 1 Structural parameters of three types of experimental projectiles |
| 横截面 形状 | 弹体 类型 | 长径比 | 长短轴 之比 | 变截面角 度/(°) | 弹体 质量/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 椭圆等截面 | E | 2.8 | 1.25 | 0 | 50.0 |
| 椭圆变截面 | VE1 | 2.8 | 1.25 | 1 | 50.0 |
| VE2 | 2.8 | 1.25 | 2.5 | 50.6 |
表2 弹体速度统计Table 2 Projectile velocity statistics table |
| 序号 | 弹体 类型 | 着角/(°) | 首层着 靶速度/ (m·s-1) | 第2层着 靶速度/ (m·s-1) | 第2层出 靶速度/ (m·s-1) | 首层靶 速度降/ (m·s-1) | 第2层靶 速度降/ (m·s-1) | 第1层速 度降低 比率/% | 第2层速 度降低 比率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E | 5 | 1034.7 | 987.6 | 929.1 | 47.1 | 58.5 | 4.55 | 5.92 |
| 2 | VE1 | 955.7 | 902.4 | 839.2 | 53.3 | 63.2 | 5.58 | 7.00 | |
| 3 | VE2 | 872.3 | 822.1 | 760.0 | 50.2 | 61.1 | 5.75 | 7.43 |
表3 弹体穿甲过程姿态统计Table 3 Attitude statistics table of projectile during armor-piercing process (°) |
| 弹体类型 | 着角 | 靶板编号 | 偏转角 | 攻角 | 姿态角 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | | Δγv | | | Δγh | α0 | α1 | Δα | θ0 | θ1 | Δθ | ||||
| E | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | -2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | -3 | -3 | 0 | 8.0 | 5.1 | -2.9 | |
| 2 | -4 | -8 | -4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 13 | 6 | 1.0 | 9.4 | 8.3 | |||
| VE1 | 1 | -5 | -7 | -2 | 6 | 12 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 6.0 | 13.0 | 7.0 | ||
| 2 | -12 | -34 | -22 | 12 | 38 | 26 | 8 | 26 | 18 | 13.6 | 37.0 | 23.4 | |||
| VE2 | 1 | -3 | -7 | -4 | 5 | 4 | -1 | 3 | 9 | 6 | 5.3 | 12.2 | 6.9 | ||
| 2 | -12 | -27 | -15 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 10 | 22 | 12 | 8.0 | 28.3 | 20.3 | |||
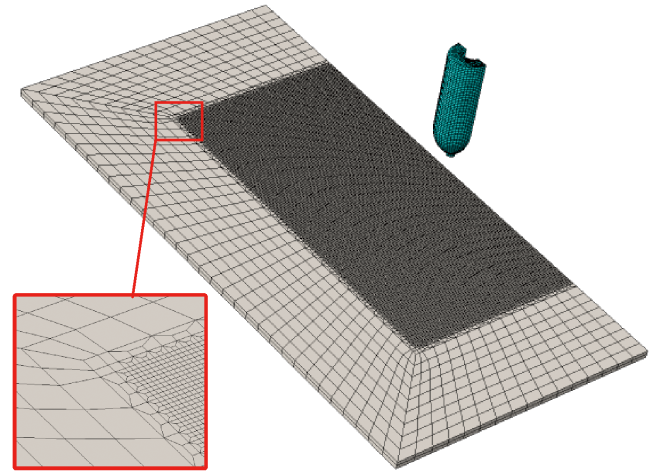
图11 弹靶有限元模型示意图Fig.11 Schematic diagram of finite element model of projectile and target |
表4 30CrMnSiNi2A材料模型参数Table 4 30CrMnSiNi2A material model parameters |
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | E/GPa | v | Tr | Tm | | χ | m | cp/(J·kg-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.85 | 210 | 0.3 | 294 | 1760 | 2.1×10-3 | 0.9 | 1 | 452 |
| A/MPa | B/MPa | n | C | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
| 1269 | 810 | 0.479 | 0.040 | 0.248 | 2.392 | 0.317 | 5.504 | -4.161 |
| 注:ρ为密度,E为弹性模量,v为泊松比, χ为塑性功转热因子,cp为定压比热容,C1~C5为待定参数。 |
表5 Q345E材料模型主要参数Table 5 Main parameters of Q345E material model |
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | E/GPa | v | A/MPa | B/MPa | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.85 | 206 | 0.28 | 355 | 930 | 0.496 |
| m | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 |
| 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.16 | -1.22 | -0.0234 | 1.5 |
| 注:ρ为密度,E为弹性模量,v为泊松比,D1~D5为J-C失效模型参数。 |
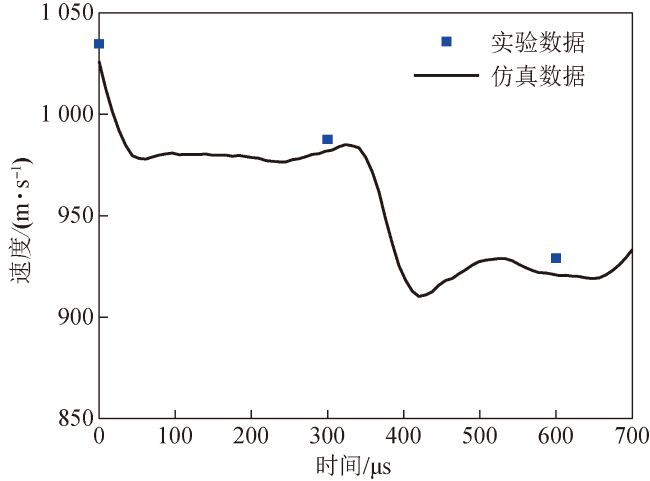
图15 速度时程曲线仿真与实验数据对比Fig.15 Speed-time curve simulation and experimental data comparison |
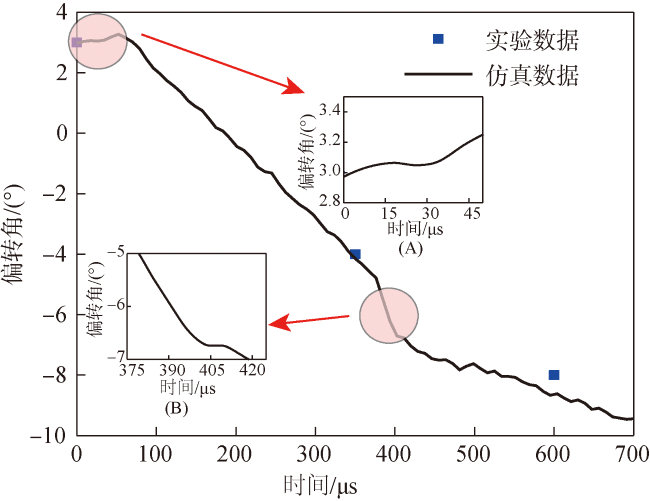
图16 偏转角时程曲线仿真与实验数据对比Fig.16 Deflection angle-time curve simulation and experimental data comparison |
表6 实验与仿真速度对比Table 6 Experimental and simulated speeds |
| 弹体类型 | 实验速度/(m·s-1) | 仿真速度/(m·s-1) | 相对误差/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 首层着靶速度 | 靶间速度 | 第2层出靶 速度 | 首层着靶速度 | 靶间速度 | 第2层出靶 速度 | 靶间速度 | 第2层出靶 |
| 1034.7 | 987.6 | 929.1 | 1034.7 | 978.1 | 916.1 | 0.96 | 1.41 | |
表7 实验与仿真偏转角对比Table 7 Experimental and simulated deflection angles |
| 弹体类型 | 实验偏转角/(°) | 仿真角度/(°) | 相对误差/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 首层着靶角度 | 第2层着靶 角度 | 第2层出靶 角度 | 首层着靶 角度 | 第2层着靶 角度 | 第2层出靶 角度 | 第2层 着靶 | 第2层 出靶 |
| 3 | -4 | -8 | 3 | -4.19 | -8.48 | 4.53 | 5.66 | |
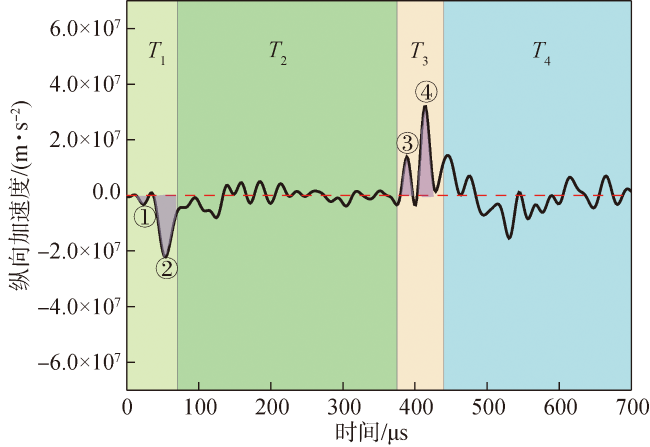
图17 E型弹体纵向加速度-时程曲线Fig.17 Longitudinal acceleration-time curve of E-type projectile |
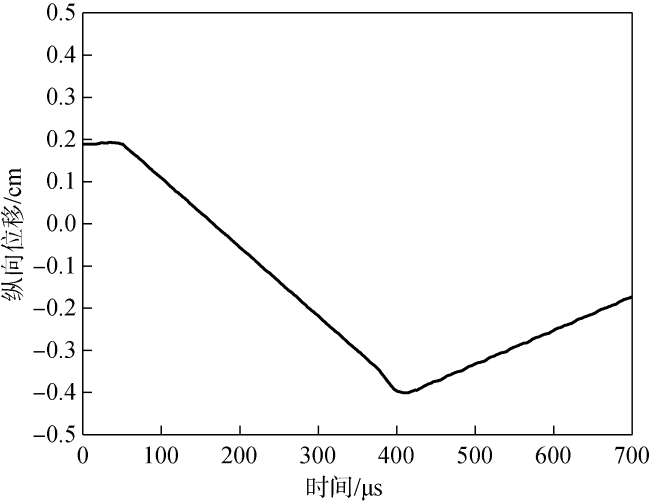
图18 E型弹体纵向位移-时程曲线Fig.18 Longitudinal displacement-time curve of E-type projectile |
表8 变截面弹体参数Table 8 Statistical table of variable cross-section projectile parameters |
| 序号 | 横截面 形状 | 变截面 角度/ (°) | 编号 | 长短轴 之比 | 弹长/ mm | 弹体 质量/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 圆等截面 | 0 | C | 1 | 42 | 50.0 |
| 2 | 圆等截面 | 1 | VC1 | |||
| 3 | 2.5 | VC2 | ||||
| 4 | 椭圆等截面 | 0 | E | 1.25 | ||
| 5 | 椭圆变截面 | 1 | VE1 | |||
| 6 | 2.5 | VE2 |
图20 弹体侵彻双层间隔钢靶数值模拟示意图Fig.20 Schematic diagram of numerical simulation of projectile penetrating double-layer spaced steel target |
| [1] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
葛超, 董永香, 陆志超, 等. 弹丸头部对斜侵彻弹道偏转影响研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(2):255-262.
通过对不同头部形状与组合材料的弹头对中厚钢靶的斜侵彻弹道对比研究,获得了尖卵形、截卵形与内凹截卵形,以及不同截卵位置、弹头长度和头部组合材料弹头对斜侵彻中弹道偏转的影响规律和侵彻过程中受到偏转力矩的变化规律。计算结果表明:截卵形弹弹道偏离角小,抗弹道姿态劣化的能力强,侵彻弹道相对稳定性好;弹头前端复合高密度、高硬度钨合金材料的弹丸侵彻能力强,弹道偏离角小。基于弹道侵彻过程偏转力矩与偏转角的时空演化特点,获得斜侵彻弹道偏转关联性。通过正交试验得到了影响弹道偏离角由大到小的因素分别为:弹头形状、弹头材料和弹速。研究结果可为低速弹丸与金属靶的斜侵彻弹道分析和弹丸头部设计提供一定帮助。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
杜华池, 张先锋, 刘闯, 等. 弹体斜侵彻多层间隔钢靶的弹道特性[J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(6):1204-1214.
为分析弹体斜侵彻多层间隔靶的弹道特性,开展典型卵形弹体不同入射角侵彻多层间隔钢靶试验和数值模拟研究。利用有限元软件LS-DYNA建立弹体斜侵彻多层间隔钢靶数值仿真模型,分析弹体斜侵彻多层间隔钢靶作用过程,得出弹体入射角、弹体速度、靶体厚度及弹体变形对多层钢靶侵彻弹道特性的影响规律并进行了试验验证。结果表明:弹体入射角越大,侵彻弹道偏转越大;初始速度越大,弹体斜侵彻多层间隔钢靶偏转角度越小,且速度对偏转角的影响幅度随速度增大呈减小趋势;随着靶体厚度增加,弹体斜侵彻多层间隔钢靶弹道由整体向下偏转转变为整体向上偏转;靶体厚度对偏转角的影响幅度随靶体厚度增大呈增大趋势;刚性弹体斜侵彻多层间隔钢靶弹道偏转角度比变形弹小。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
The elliptical cross-section ogive-nose projectile (ECOP) has recently attracted attention because it is well suited to the flattened shape of earth-penetrating weapons. However, the penetration performance of ECOPs has not been completely understood. The objective of this study was to investigate the penetration performance of ECOPs into concrete targets using a theoretical method. A general geometric model of ECOPs was introduced, and closed-form penetration equations were derived according to the dynamic cavity-expansion theory. The model was validated by comparing the predicted penetration depths with test data, and the maximum deviation was 15.8%. The increment in the penetration depth of the ECOP was evaluated using the proposed model, and the effect of the major–minor axis ratio on the increment was examined. Additionally, the mechanism of the penetration-depth increment was investigated with respect to the caliber radius head, axial stress, and resistance. © 2020 The Authors
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [15] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [16] |
朱超, 张晓伟, 张庆明, 等. 弹体斜侵彻双层钢板的结构响应和失效研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(9):140-154.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [17] |
李东伟, 刘俞平, 王筱锋, 等. 弹形参数对战斗部斜穿甲姿态偏转影响研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2021, 42(9):40-44.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [18] |
田泽, 王浩, 武海军, 等. 椭圆变截面弹体斜贯穿薄靶姿态偏转机理[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(7):1537-1552.
随着新型武器平台的发展,具有良好平台适应性、高升阻比及隐身性能等特点的异形截面(椭圆形及变截面椭圆形)战斗部开始受到广泛关注。为探究椭圆变截面弹体斜贯穿薄靶机理与姿态偏转规律,对3种不同截面(圆形、椭圆形、变截面椭圆形)弹体斜贯穿双层945舰船薄钢板实验过程及结果进行整理与分析,根据椭圆变截面弹体贯穿过程、靶板破坏失效模式与弹体受力特征,将贯穿过程分为弹体头部压入阶段、弹体头部贯穿阶段、过渡阶段与弹身贯穿阶段。基于能量守恒、虚功原理分阶段分析弹体受力特征,建立弹体姿态偏转理论模型。通过对已有实验和数值模拟结果与理论模型所得结果进行对比,验证理论模型的可靠性。采用该理论模型着重讨论弹体撞击速度、初始倾角、质心位置、弹体翻滚角及椭圆截面长短轴之比等参数对椭圆变截面弹体姿态偏转的影响。结果表明:随着椭圆变截面弹体初始撞击速度的增加,弹体姿态偏转角度呈现指数型减小趋势;随着椭圆变截面弹体初始倾角的增大,弹体姿态偏转量增大;随着椭圆变截面弹体质心位置的后置,弹体姿态偏转角度增大;椭圆变截面弹体以不同的翻滚角撞击靶板时,弹体姿态偏转角度不同,γ<sub>pt</sub>=0°较γ<sub>pt</sub>=90°时弹体姿态偏转角度更大;当γ<sub>pt</sub>=0°时,椭圆变截面弹体椭圆截面长短轴之比增大,弹体姿态偏转角度随之增大;当γ<sub>pt</sub>=90°时,规律则相反。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [19] |
邓希旻, 田泽, 武海军, 等. 上下非对称结构弹体侵彻金属薄板的特性及薄板破坏形式[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12):3836-3850.
为支撑超高声速导弹终点毁伤理论设计,适应异型弹体穿甲力学基础理论发展需求,非对称异型弹体贯穿金属薄板的穿甲特性及靶板损伤机理是当前亟需解决的关键科学问题。开展上下非对称结构异型弹体正/斜贯穿多层间隔921A薄钢板实验,基于Abaqus/Explicit、VUMAT和Python子程序开展数值模拟研究,分析弹体速度变化及偏转特性,结合靶板破坏形貌和能量耗散分析靶板损伤机理,讨论了研究结果在实际工程应用中的适用性。研究结果表明:上下非对称结构异型弹体具有维持弹体姿态稳定的特点,初速低于600m/s时速度降和弹道极限随倾角的增加而增大,靶板破坏模式以剪切冲塞、瓣裂和整体横向变形主导,初速高于600m/s时同初始倾角的弹道极限曲线重合,无量纲速度降随初速增加而降低,靶板破坏模式向延性扩孔、瓣裂和破碎转变;靶板塑性变形时切向塑性功占比最大、环向塑性功最小、轴向和径向塑性功相近,高速侵彻过程中靶板碎片动能为塑性功的25%~50%;基于几何相似的缩比模型可反映原型弹体高速穿甲时的速度变化情况及靶板的毁伤特性;研究成果可为异型弹体高速穿甲的弹靶响应及阻力特性的理论建模提供物理认识及数据支撑。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [20] |
李磊. 不同硬度30CrMnSiNi2A钢动态本构与损伤参数研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2017.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [21] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
余万千, 郁锐, 崔世堂, 等. 考虑应力三轴度影响的30CrMnSiNi2A钢韧性断裂研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(3):47-54.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(23699 KB)
PDF(23699 KB)
 图1 变截面弹体结构特征图
图1 变截面弹体结构特征图 图2 变截面弹体结构参数图
图2 变截面弹体结构参数图 表1 3类实验弹体结构参数
表1 3类实验弹体结构参数 图3 实验弹体实物图
图3 实验弹体实物图 图4 发射件示意图
图4 发射件示意图 图5 实验靶板系统
图5 实验靶板系统 图6 实验平台示意图
图6 实验平台示意图 图7 弹体偏转角示意图
图7 弹体偏转角示意图 表2 弹体速度统计
表2 弹体速度统计 图8 弹体侵彻靶板的弹道轨迹图
图8 弹体侵彻靶板的弹道轨迹图 表3 弹体穿甲过程姿态统计
表3 弹体穿甲过程姿态统计 图9 第2层靶板破坏形貌图
图9 第2层靶板破坏形貌图 图10 回收弹体及冲塞块图
图10 回收弹体及冲塞块图 图11 弹靶有限元模型示意图
图11 弹靶有限元模型示意图 图12 网格敏感性验证
图12 网格敏感性验证 表4 30CrMnSiNi2A材料模型参数
表4 30CrMnSiNi2A材料模型参数 表5 Q345E材料模型主要参数
表5 Q345E材料模型主要参数 图13 仿真靶板破坏形貌图
图13 仿真靶板破坏形貌图 图14 仿真与实验弹道轨迹图
图14 仿真与实验弹道轨迹图 图15 速度时程曲线仿真与实验数据对比
图15 速度时程曲线仿真与实验数据对比 图16 偏转角时程曲线仿真与实验数据对比
图16 偏转角时程曲线仿真与实验数据对比 表6 实验与仿真速度对比
表6 实验与仿真速度对比 表7 实验与仿真偏转角对比
表7 实验与仿真偏转角对比 图17 E型弹体纵向加速度-时程曲线
图17 E型弹体纵向加速度-时程曲线 图18 E型弹体纵向位移-时程曲线
图18 E型弹体纵向位移-时程曲线 图19 弹体穿靶不同阶段图
图19 弹体穿靶不同阶段图 表8 变截面弹体参数
表8 变截面弹体参数 图20 弹体侵彻双层间隔钢靶数值模拟示意图
图20 弹体侵彻双层间隔钢靶数值模拟示意图 图21 弹体速度时程曲线图
图21 弹体速度时程曲线图 图22 弹体纵向位移时程曲线图
图22 弹体纵向位移时程曲线图 图23 弹体偏转角时程曲线图
图23 弹体偏转角时程曲线图 图24 不同截面弹体纵向加速度时程曲线图
图24 不同截面弹体纵向加速度时程曲线图 图25 弹体穿靶过程示意图
图25 弹体穿靶过程示意图/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |