

一种刚柔混合弦向变弯度机翼后缘设计
Design of Trailing Edge of a Rigid-flexible Chord-Wise Variable Camber Wing

为实现机翼在驱动控制下实现弦向连续弯度变化,同时考虑材料变形能力,提出一种刚柔混合式变后缘翼型。通过对翼型中弧线进行几何分析,建立变弯度构型参数化模型,并以升阻比为优化目标,计算最优的刚性段下弯角度以及柔性段下弯曲线。利用计算流体力学计算,对比不同攻角下,刚柔混合偏转翼型和传统刚性偏转翼型的升力系数、升阻比等气动特性。以巡航时单位展长所要求升力为优化目标,分别求解低速巡航及降落两种工况下,两种不同后缘翼型的下弯角度及变形方式。对比两种下偏方式的压力分布、速度分布、气流分离位置等流场特性。根据优化构型制造刚柔混合式变后缘机翼模型,并进行变形能力测试。计算结果表明:刚柔混合后缘翼型在同等偏角下,具有更高的升力系数、升阻比,更优的气动特性;而在相同的飞行工况下,刚柔混合后缘翼型下偏角度要求更小,气流分离点更靠后,具有更高的气动效率。通过变形能力试验验证了柔性翼肋结构及蒙皮设计的合理性。
In order to realize the continuously chord-wise camber change of a wing under driving control, with material deformation ability considered,, an airfoil with hybrid (rigid-flexible) variable trailing edge is proposed. Through the geometric analysis of the mean camber line of the trailing edge, the parametric model of variable camber configuration is established. Taking lift-drag ratio as the optimization objective, the optimal bending angle of the rigid section and the optimal curve of the flexible section are calculated. The lift coefficient, lift-drag ratio and other aerodynamic characteristics of the rigid-flexible airfoil and traditional rigid airfoil are compared at different angles of attack by CFD calculation. When the lift required by the unit span during cruise is taken as the optimization objective, the bending angles and deformation modes of two different trailing edge airfoils are solved respectively in low-speed cruise condition and landing condition. The pressure distribution, velocity distribution and separation position of the two bending forms are compared. A wing model with rigid-flexible variable trailing edge based on the optimized configuration is fabricated and the deformation capability testing is conducted. The results show that: the rigid-flexible trailing edge airfoil has higher lift coefficient, lift-drag ratio and better aerodynamic characteristics in same deflection angle; in the same flight condition, the rigid-flexible trailing edge airfoil has a smaller deflection angle and a more backward separation point, so it has a higher aerodynamic efficiency. The rationality of the flexible wing rib structure and skin design has been verified through deformation capability testing.
弦向变弯度机翼 / 翼型中弧线 / 刚柔混合 / 升阻比 / 变后缘机翼模型 {{custom_keyword}} /
chord-wise variable camber wing / mean camber line of airfoil / rigid-flexible / lift-drag ratio / variable trailing edge wing model {{custom_keyword}} /
表1 翼型状态及环境参数Table 1 Airfoil state and operating parameters |
| 攻角/ (°) | 马赫数 | 空气密度/ (kg·m3) | 空气动力黏度/ (Pa·s) | 雷诺数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.2 | 1.205 | 1.78938×10-5 | 4.58×106 |
表2 刚柔混合翼型后缘偏转构型Table 2 Configuration of rigid-flexible trailing edge of airfoil |
| 飞行工况 | 攻角/ (°) | 马赫数 | 高度/ m | 刚性偏 角/(°) | 柔性偏 角/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低速巡航 | 4 | 0.35 | 100 | 0 | 8.7 |
| 降落工况 | 8 | 0.2 | 0 | 3.78 | 15 |
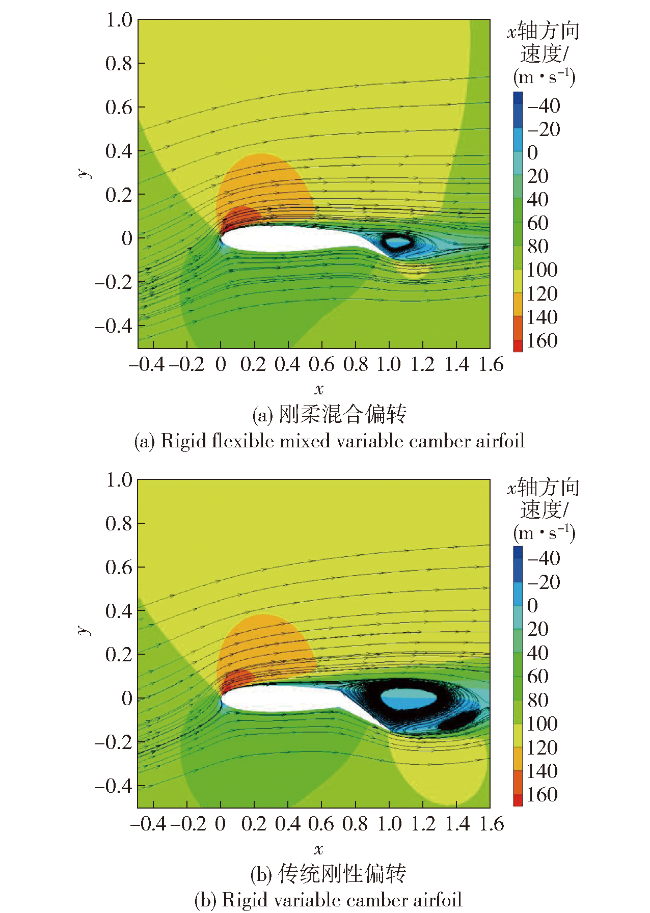
图12 降落工况速度云图及流线对比Fig.12 Comparison of velocity nephogram and streamline of landing |
| [1] |
刘卫东. 变形机翼关键技术的研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
王彬文, 杨宇, 钱战森, 等. 机翼变弯度技术研究进展[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(1):144-163.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [15] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [16] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [17] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [18] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [19] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [20] |
杨超, 陈桂彬, 邹丛青. 主动气动弹性机翼技术分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 1999, 25(2):171-175.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [21] |
刘卫东, 丁倩, 朱华, 等. 基于超声电机的变弯度翼的驱动与集成[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2013, 33(5):856-861.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
张音旋, 邱涛, 王健志. 一种柔性蒙皮设计技术及其在后缘变弯度机翼结构中的应用[J]. 航空科学技术, 2012(5):26-28.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [23] |
杨智春, 解江. 柔性后缘自适应机翼的概念设计[J]. 航空学报, 2009, 30(6): 1028-1034.
对H.P.Monner提出的 “可转动翼肋”自适应机翼概念进行运动学研究,推导了驱动位移量和偏转变形量之间的对应关系。这种可变形翼肋可简化为由平面连杆机构组合而成的单自由度系统,能使机翼后缘柔性偏转的同时保持翼面光滑连续。提出了基于曲线逼近原理根据后缘中弧线偏转轨迹优化转轴点布局的翼肋机构设计方法。对悬臂梁型、圆弧型和反悬臂梁型3种偏转距离相等但偏转轨迹不同的柔性后缘进行了方案设计和分析,从翼肋机构的实现、承载能力以及气动特性3方面进行了建模计算和比较研究。结果表明,圆弧型是3种柔性后缘中最佳的设计方案;柔性后缘自适应机翼的设计分析方法是切实可行的,可根据实际需要设计出满足任意后缘偏转要求的自适应机翼。
A concept design based on the rotating rib proposed by H.P.Monner is conducted to implement the variable camber adaptive wing concept by means of deforming the trailing edge flexibly with continued and smooth contour. A study is made of the kinematics of the rib structure, which can be simplified as a single degree- of freedom (DOF) leverage system constrained by pivot joints. The pivot location optimization by curve approximation is proposed to design the flexible trailing edge to meet the design requirements. To test the feasibility of the proposed concept design method, a 2D wing model characterized by NACA63015A airfoil with 1000 mm length in chordwise direction is utilized as a benchmark. The maximum deflection displacement of the tip point on the trailing edge as required by the design is 62 mm. Three types of cambered trailing edges with the same tip point deflection displacement but different deflection tracks, i.e., the beam type, the arc of circle type, and the inverse beam type, are introduced. A comparative study is performed in terms of structure realization, load carrying capability, and aerodynamic performance. The result shows that the model-configured with the arc of circle type trailing edge has the best performance and the design method is feasible and practical. It can be applied to any other design proposals of trailing edge deflection based on specific requirements. {{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [24] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [25] |
冷劲松, 孙健, 刘彦菊. 智能材料和结构在变体飞行器的应用现状与前景展望[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(1): 29-45.
变体飞行器可以根据不同的飞行条件改变自身形状以获得最优的气动性能,大大提高飞行器的综合性能,是未来飞行器发展的重要方向之一。新型智能材料和结构具有驱动、变形、承载、传感等特点,为变体飞行器的设计提供了新的技术途径。本文根据不同可变形机翼结构分类,详细阐述了智能材料和结构在自适应结构、智能驱动器和变形蒙皮等方面的研究现状。变体飞行器的实现亟需解决变形/承载一体化蒙皮技术、轻质大输出力驱动器技术和自适应结构技术等关键技术,本文还对智能材料和结构未来在变体飞行器上的应用前景进行了展望。
Morphing aircraft can alter their shapes to achieve optimal aerodynamic performance under different flight conditions, which will greatly improve the comprehensive performance of the aircraft. Their emergence and development is one of the most important trends of future aircraft. Smart materials and structures have the properties of actuating, morphing, loading, sensing etc., which provide a new technological approach to morphing aircraft design. In this paper, research status is elaborated of smart materials and structures in adaptive structures, smart actuators, and morphing skins. Some key technologies are addressed in detail, such as deformation/loading integrative skins, lightweight high-output actuators, and adaptive structures. The future prospect of the application of smart materials and structures in morphing aircraft is also discussed. {{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [26] |
陈秀, 葛文杰, 张永红, 等. 基于遗传算法的柔性机构形状变化综合优化研究[J]. 航空学报, 2007, 28(5): 1230-1235.
实现机翼在不同的飞行状态下的最优气动外形是变弯度自适应机翼的一项关键技术。针对传统铰链机构会使机翼表面产生不连续变化而导致气流提早分离的问题,从全柔性机构实现连续平滑的形状变化的技术出发,以目标形状与实际形状的边界曲线之差最小为优化目标,采用遗传算法(GA)对柔性机构的拓扑、尺寸、形状进行了综合优化。在优化方法上,以二进制编码技术和实数编码技术为基础建立初始离散柔性机构的混合变量遗传算法模型,将其映射为有限元模型并进行了结构分析。在优化过程中引入了渐进结构优化(ESO)算法的思想,消除GA优化过程中产生的自由单元,改善了优化效率和分析结果。结合机翼前缘形状变化实例,基于MATLAB进行优化设计,并用ANSYS10.0对优化结果进行了机构的仿真分析。分析结果表明,所提出的方法合理、有效。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [27] |
徐钧恒, 杨晓钧, 李兵. 基于交叉簧片式铰链的变弯度机翼机构设计[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2022, 56(3):444-451, 509.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [28] |
王宇, 黄东东, 郭士钧, 等. 变体机翼后缘多学科设计与优化[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 53(3):415-424.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [29] |
尉濡恺, 戴玉婷, 杨超, 等. 基于变弯度后缘的机翼阵风响应减缓数值研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(7):1864-1874.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [30] |
陈钱, 白鹏, 尹维龙, 等. 可连续光滑偏转后缘的变弯度翼型气动特性分析[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2010, 28(1): 46-53.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [31] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [32] |
聂瑞, 裘进浩, 季宏丽, 等. 主动柔性后缘气动特性优化[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2019, 40(1): 69-76.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [33] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [34] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [35] |
李宝仁, 刘军, 杨钢. 气动人工肌肉系统建模与仿真[J]. 机械工程学报, 2003, 39(7): 23-28.
建立了气动人工肌肉系统完整的静动态特性数学模型,提出气动人工肌肉系统的工作过程可以分为等容充气、充气收缩、排气伸长和等容排气四个部分。并通过仿真分析了气动人工肌肉系统的工作特性,为控制策略的选取以及试验研究打下基础。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [36] |
王斌锐, 靳明涛, 沈国阳, 等. 气动肌肉肘关节的滑模内环导纳控制设计[J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(6): 1233-1238.
柔顺控制是共融机器人研究的重点。针对级联式气动肌肉肘关节动力学模型,建立了以滑模位置控制为内环、触力导纳控制为外环的控制结构;设计了带干扰观测器的滑模控制器(SMCDO),证明SMCDO算法的收敛性;将环境等效为弹簧模型,设计了外环导纳控制器,并给出控制律。搭建实物测试平台,分别开展阈值力、力安全阈值测试以及碰撞测试,并分析了刚度系数对修正轨迹和接触力的影响。实验结果表明:关节柔顺性与刚度系数相关;SMCDO内环导纳控制精度优于无干扰观测器的滑模控制器内环导纳控制;所设计的控制算法稳定且有效。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 图1 翼肋后缘结构布局示意图
图1 翼肋后缘结构布局示意图 图2 翼型后缘中弧线
图2 翼型后缘中弧线 表1 翼型状态及环境参数
表1 翼型状态及环境参数 图3 最优翼型优化流程图
图3 最优翼型优化流程图 图4 柔顺翼肋最优变弯度构型
图4 柔顺翼肋最优变弯度构型 图5 刚柔混合型与悬臂梁型变弯度构型对比
图5 刚柔混合型与悬臂梁型变弯度构型对比 图6 计算网格
图6 计算网格 图7 升力系数对比
图7 升力系数对比 图8 升阻比系数对比
图8 升阻比系数对比 表2 刚柔混合翼型后缘偏转构型
表2 刚柔混合翼型后缘偏转构型 图9 低速巡航工况压力云图对比
图9 低速巡航工况压力云图对比 图10 低速巡航工况速度云图及流线对比
图10 低速巡航工况速度云图及流线对比 图11 降落工况压力云图对比
图11 降落工况压力云图对比 图12 降落工况速度云图及流线对比
图12 降落工况速度云图及流线对比 图13 降落工况翼型上下表面压力系数对比
图13 降落工况翼型上下表面压力系数对比 图14 基于载荷路径法的拓扑优化流程
图14 基于载荷路径法的拓扑优化流程 图15 柔顺段拓扑优化设计区域示意图
图15 柔顺段拓扑优化设计区域示意图 图16 刚柔混合后缘结构
图16 刚柔混合后缘结构 图17 刚柔混合变弯度翼型压力系数
图17 刚柔混合变弯度翼型压力系数 图18 刚性段抽拉式蒙皮设计
图18 刚性段抽拉式蒙皮设计 图19 翼肋末端处上下翼面连接结构
图19 翼肋末端处上下翼面连接结构 图20 刚柔混合变后缘模型
图20 刚柔混合变后缘模型 图21 不同驱动下后缘变形形态
图21 不同驱动下后缘变形形态/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |