 PDF(10539 KB)
PDF(10539 KB)


Interior Trajectory Characteristics of Underwater Ejection Using a Flexible Piston Rod Driven by Water Pressure
DINGYanchao, HEZhenmin, ZHANGZhe, HANWenji, WUWenting
 PDF(10539 KB)
PDF(10539 KB)

Sponsored by: China Association for Science and Technology (CAST)
Editor-In-Chief: Xu Yida
ISSN 1000-1093
Hosted By: China Ordnance Society
Published By: Acta Armamentarii
CN 11-2176/TJ
 PDF(10539 KB)
PDF(10539 KB)
Interior Trajectory Characteristics of Underwater Ejection Using a Flexible Piston Rod Driven by Water Pressure
In order to meet the requirements of unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV) launching the torpedos,a new underwater ejection scheme with flexible piston rod is proposed.In the ejection scheme,the high pressure in large depth environment is used to drive the piston to launch a torpedo.An interior trajectory calculation model of torpedo launched from the ejection device with flexible piston rod is established.And the model is verified by the principle test in the high pressure water tank laboratory.The different launching schemes in the related literatures are comparatively studied based on the model.The results show that the ejection scheme with flexible piston rod has the characteristics of smooth acceleration without steep change,large effective acceleration stroke and high pipe exit speed compared with the traditional multistage cylinder launching scheme.Compared with the traditional high-pressure gas-driven piston scheme,the high-pressure water-driven piston scheme is simpler in structure without pressure storage device.A piston buffer scheme based on load reduction in steps proposed in the paper has better load reduction effect compared with the traditional throttle hole buffer scheme.And it won’t cause excessive pressure in the reverse cavity of piston cylinder.Under the ambient pressure of 1.1-6.1MPa,the predicted velocity of torpedo exiting tube varies from 7.0 to 11.6m/s,and the rear reference point of torpedo dose not collide with the tube wall.The results verify the feasibility of the underwater ejection scheme with flexible piston rod,which provides the design basis for the further development of ejection device.
unmanned underwater vehicle / torpedo / water drive / flexible piston rod / interior trajectory modeling {{custom_keyword}} /

Table 1 The parameters of ejection device表1 弹射装置参数 |
| 参数 | 原理试验数值 | 水下弹射仿真数值 |
|---|---|---|
| L/m | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| S1/cm2 | 50.3 | 50.3 |
| S2/cm2 | 50.3 | 50.3 |
| S3/cm2 | 39.3 | 32.2 46.4 63.1 |
| t/s | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 注:L为鱼雷长度。 |
Table 2 Initial values of input variables表2 控制变量参数初值 |
| 参数 | 原理试验数值 | 水下弹射仿真数值 |
|---|---|---|
| pa、p1、p2/MPa | 0.22 | 1.1 3.1 6.1 |
| p3/MPa | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Δ1/cm3 | 0 | 0 |
| Δ2/cm3 | 12566 | 12566 |
| dt/s | 0.15 | 0.15 |
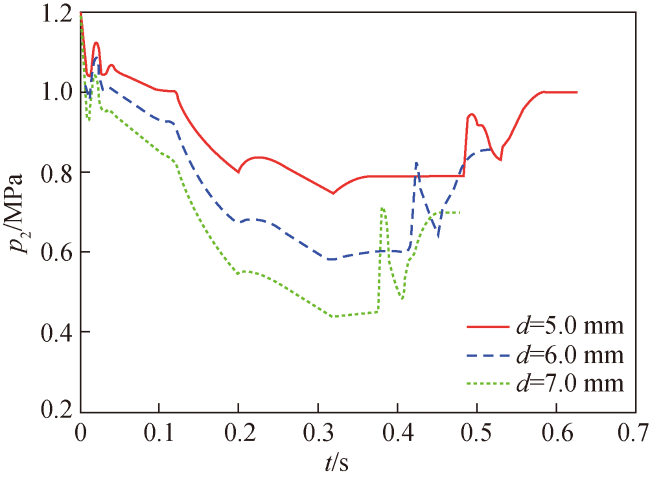
Fig.6 Pressure p2 in reverse cavity of piston cylinder in different drainage hole schemes图6 不同排水孔方案活塞缸反腔压力p2曲线 |
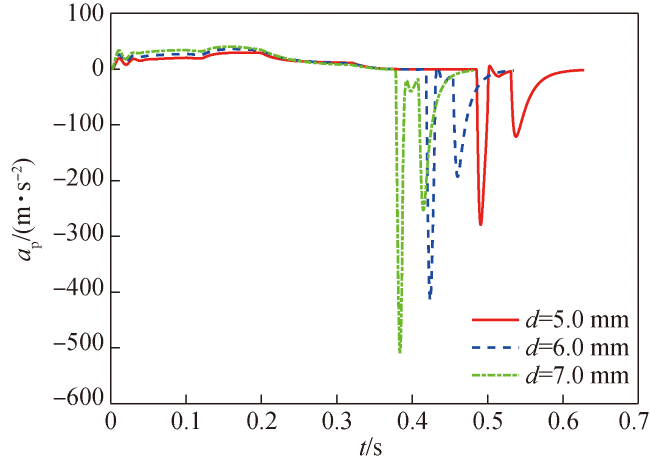
Fig.8 Acceleration ap of piston in different drainage hole schemes图8 不同排水孔方案活塞加速度ap变化曲线 |
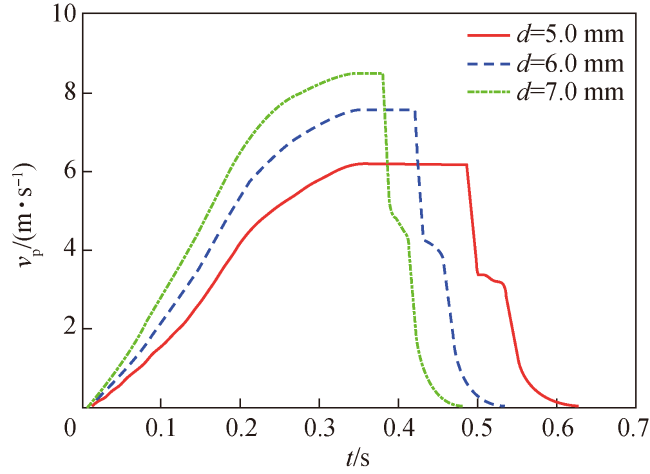
Fig.9 Velocity vp of piston in different drainage hole schemes图9 不同排水孔方案活塞运动速度vp曲线 |

Fig.11 Velocity vp of piston under different ambient pressures图11 不同环境压力状态活塞运动速度vp变化曲线 |
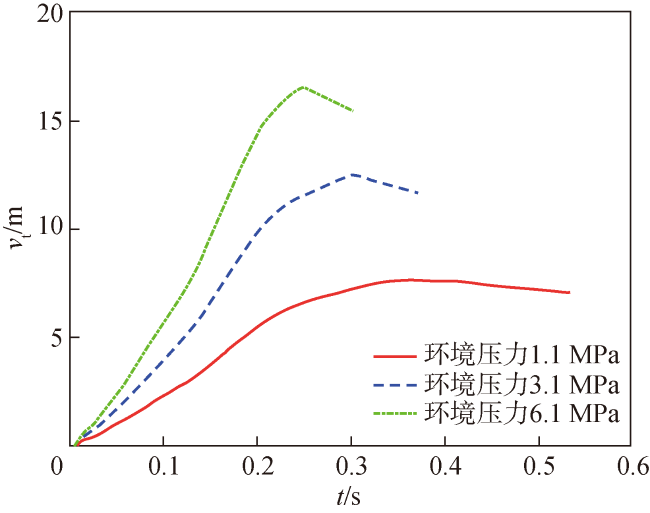
Fig.13 Velocity vt curves of torpedo under different ambient pressures图13 不同环境压力状态鱼雷运动速度vt变化曲线 |
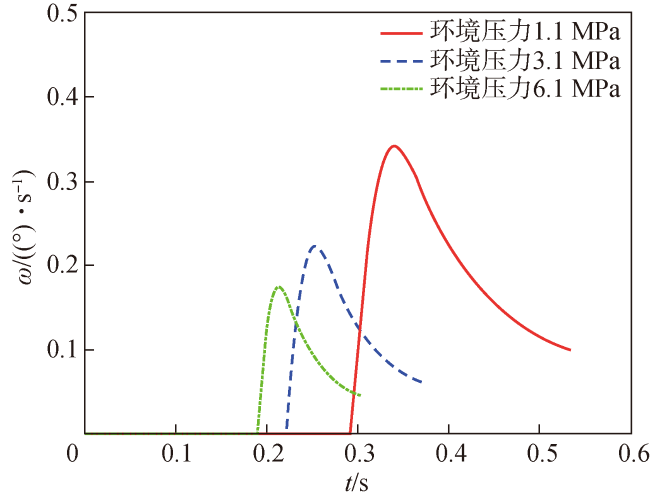
Fig.14 The rate of pitch angle ω of torpedo under different ambient pressures图14 不同环境压力状态鱼雷俯仰角速度ω变化曲线 |
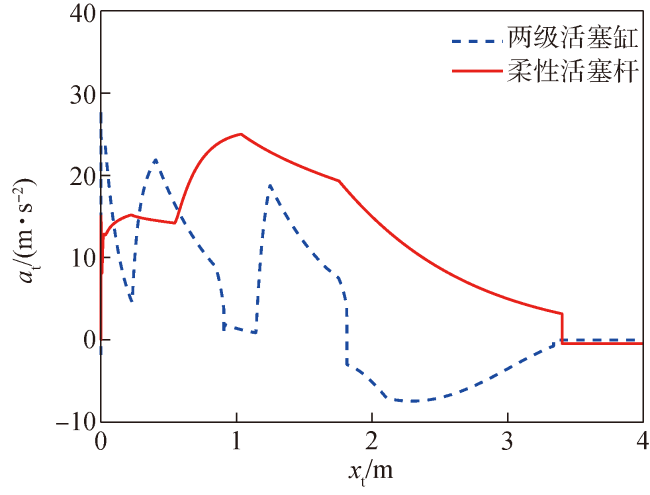
Fig.23 Acceleration at of torpedo in different ejection schemes图23 不同弹射方案鱼雷加速度at变化曲线 |
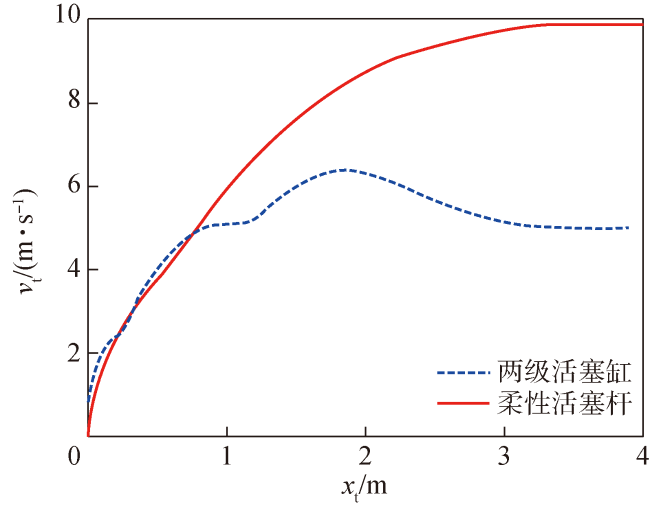
Fig.24 Velocity vt of torpedo in different ejection schemes图24 不同弹射方案鱼雷运动速度vt变化曲线 |
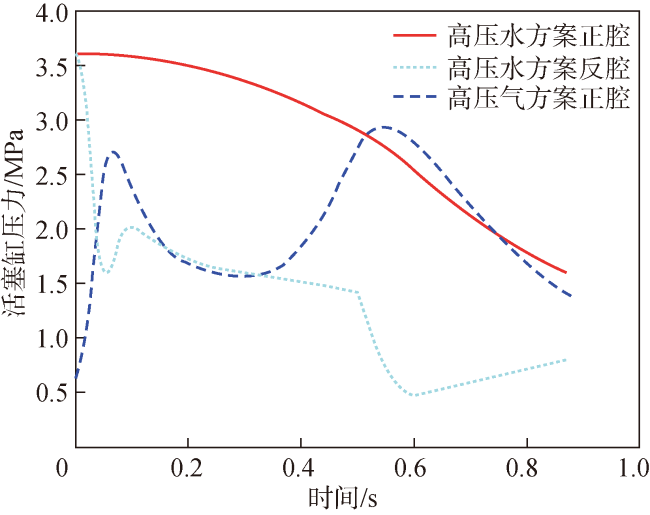
Fig.26 Pressure curves of piston cylinders with different working media图26 不同工质活塞缸腔内压力变化曲线 |
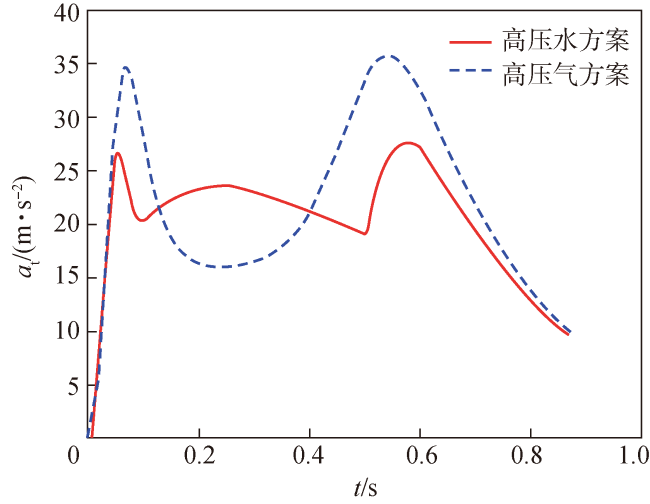
Fig.27 Acceleration at of torpedos with different working media图27 不同工质鱼雷加速度at变化曲线 |
| [1] |
练永庆, 王树宗, 李宗吉, 等. 鱼雷弹射装置设计原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012:154-155.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
杨弓熠, 詹磊, 贾轩, 等. UUV冲压活塞式装置发射鱼雷内弹道特性研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(6):903-910.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
曾培高, 姜毅, 杨哩娜. 上浮式水面发射筒弹射内弹道特性[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(6):1266-1276.
为研究新型上浮式水面发射筒弹射内弹道特性及其影响因素,采用Realizable k-ε湍流模型、Mixture多相流模型以及动态分层技术,建立考虑上浮速度影响的弹、筒弹射模型。对弹筒模型在水面与地面上的弹射过程分别进行数值模拟,对比分析二者的内弹道性能与筒内流动变化规律,并研究发射筒出水速度对水面发射内弹道性能的影响。对比结果表明,水面发射的弹、筒相对运动快于地面发射的相对运动,使得水面发射的燃气做功用时比地面发射的用时少14%,水面发射弹体受到的最大载荷比地面发射小20%;由于水面发射中发射筒具有相对较高的设定出水速度,水面发射弹体的出筒速度大于地面发射的出筒速度。流动分析表明:在设定的出水速度条件下,水面发射过程中燃气不会直接与水面发生作用,无相变耗能过程。影响因素分析表明,在安全发射条件下,出水速度主要通过改变水对筒的作用力来影响弹、筒的相对运动速度,但燃气对筒的作用力远远大于水对筒的作用力,使得出水速度对弹、筒相对运动的非线性影响几乎可以忽略,出水速度的改变几乎不会影响弹体的出筒速度增量。
The Realizable k-ε turbulence model,the mixture multiphase model and the dynamic layering mesh update method are used to investigate the interior ballistics of a new independent water-surface launching canister,and analyze its influencing factors by modeling the relative motion between the missile and the canister. The interior ballistics and the internal flow characteristics of canister launcher on water-surface and ground are analyzed and compared numerically,and the influence of the canister emerging velocity on the interior ballistics is investigated. Results show that the launchers on water-surface and ground have the similar flow characteristics in the gaps and in the pressures in the low pressure chambers. The exit velocity of the missile on water-surface is faster than that on ground,the maximum missile load on water-surface is 20% less than that on ground,and the launch time for the water-surface launching is 14% less than that on ground.The flow results show that the gas does not directly interact with the water surface,therefore the phase change energy dissipation does not happen.The emerging velocity changes the ejection velocity increment by affecting the force of water on the canister.The nonlinear effect of the emerging velocity on the increment of ejection velocity can be ignored because the buoyancy variation is far less than the gas force,so the exit velocity of missile is a linear superposition of the emerging velocity and the increment of ejection velocity.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
练永庆, 李春来, 李宗吉. 水下橡胶弹性弹射鱼雷内弹道仿真[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2016, 28(6):100-106.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
徐勤超, 潘海兵, 练永庆, 等. 提拉缸式鱼雷弹射装置内弹道建模与试验[J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(11):2259-2265.
为解决水面舰艇鱼雷发射作战准备时间长,载弹保障能力差的问题,提出了一种水面舰艇提拉缸式鱼雷发射装置方案。采用Simulink和Adams联合仿真的方式,建立发射装置高压空气发射过程的动力学模型,进行仿真分析,并基于小型原理样机对仿真结果进行了试验验证。仿真和试验结果表明:在气瓶压力为25 MPa时,发射过程中提拉缸峰值压力为9.3 MPa,整个装置零部件间最大接触力为66.6 kN,鱼雷出管速度达到14.7 m/s,最大加速度为236 m/s<sup>2</sup>,发射时间为0.14 s;研究结果验证了以提拉缸为动力组件的轻型鱼雷发射方案是可行的。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
陈尚成, 冯文正, 姜涛, 等. 无人机水下弹射试验系统弹射性能的仿真研究[J]. 机床与液压, 2023, 51(16):172-177.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
陈哲, 郭翔, 余瑞, 等. 活塞式水平弹射装置内弹道性能研究[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2022, 45(2):316-321.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
丁彦超, 王宝寿, 吴文婷, 等. 水压驱动两级提拉式水下弹射内弹道建模[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(2):594-605.
针对大深度环境水下发射技术需求,提出一种利用水压驱动两级提拉式水下新型发射方案。利用大深度环境高压水驱动两级活塞实现武器快速发射。建立武器出管过程动力学模型,开展高压水驱动方案原理验证试验,并与高压气体驱动方案进行了对比分析。研究结果表明:水压驱动与气体驱动方案的内弹道结果基本一致,高压水发射方案在大深度环境具有显著优势;加速度峰值出现在发射瞬时和级间转换过程,级间转换过程武器加速度存在显著的陡变现象;水下发射武器出管过程弹道预报结果得出,在发射水深100~500m条件下,武器出管过程最大速度范围为 7.4~15.3m/s,最大加速度小于100m/s<sup>2</sup>;研究结果验证了水压驱动两级活塞式发射方案的可行性,为装置的进一步研制开发提供了设计依据。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
姚琳, 马大为, 马吴宁, 等. 两级提拉式单侧弹射装置内弹道建模与优化[J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(3):466-475.
为延长导弹压缩空气弹射的有效推力行程,提出一种新型两级提拉式单侧冷弹射方案。采用Peng-Robinson真实气体方程,建立了弹射内弹道模型;在Simulink中搭建内弹道求解模块、在ADAMS中建立了冷弹射方案的虚拟样机,以气缸输出力、气缸位移和速度为状态变量,实现联合仿真,获得了内弹道参量的变化规律,并基于小型原理样机试验对仿真结果进行了验证。验证结果表明:第1级低压室压强先升后降;气缸换级过程中,低压室温度、压强与导弹加速度发生突变,但对导弹速度、位移影响较小。以气源容积最小为目标函数,选定约束条件和设计变量,应用遗传算法进行优化设计。优化后的气源容积降低了64.5%,优化结果大大提高了发射装置的机动性。研究结果验证了新型两级提拉式单侧冷弹射方案的可行性。
A kind of one-side ejection device with two-step cylinder is proposed to increase the effective thrust travel of missile pneumatic launching system. The real gas state equation, Peng-Robinson equation, is used as theoretical basis. The mathematical expressions of pneumatic interior ballistics model are deduced on the basis of 'P-R' state equation for the two-step cylinder. The interior ballistics equation is solved by using Simulink software, and the one-side launching ejection is built by means of ADAMS. The co-simulation model of device is achieved. The results show that the pressure of first-order lower-chamber rises first and then falls. It can be seen from the calculated result that both the thermodynamic parameters and the missile acceleration obviously fluctuate in the process of cylinder changing, but their influences on missile speed and displacement are very small. To reduce the equipment volume, the air source volume is selected as the objective function. The air source volume optimized by genetic algorithm is decreased by 64.5%, thus improving greatly the mobility of launcher. Key
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
宋满存, 李国强, 朱熠, 等. 一种多级结构的浮力调节装置及其精度分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(9):120-125.
浮力调节装置可用于无人潜航器的浮力控制,使其节能地实现上浮、下潜或悬停等功能。文中基于5级缸结构设计了一款大容积高精度的液压油容积式浮力调节装置,通过位移传感器监控活塞位置并对多级缸伸缩特性进行假设,得到了浮力分段解算方法和最大可能误差范围;通过样机研制与试验,验证了多级缸在磨合后趋于伸缩特性假设的事实,同时对浮力分段解算方法进行了优化拟合,大幅提高了该浮力调节装置的精度。试验证明,文中样机可以满足0~80L浮力连续可调、1L最小调节步长、综合调节精度不低于0.5%FS的指标要求。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
唐垚, 姜毅, 王成德, 等. 多级活塞缸式燃气弹射内弹道的研究[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2018, 41(4):524-531.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [15] |
郭锦炎, 竺伊文, 王华吉, 等. 某多级杆式空气弹射系统内弹道仿真与试验研究[J]. 弹道学报, 2022, 34(1):72-76.
为了满足某多级杆式空气发射系统的研制需要,建立了多空气瓶动力源时序开阀供气的多级杆发射系统的内弹道仿真模型,设计了模型正确性验证试验方案,开展了该系统的内弹道仿真与试验研究。描述了多级杆式空气发射系统的设计原理,根据该发射系统的工作原理,借鉴经典枪炮零维内弹道模型,建立了该空气发射系统弹射过程的内弹道模型,进行了通用工况的仿真模型研究。设计了多级杆式空气发射系统内弹道模型正确性校验试验方案,开展了3 000 kg配重的弹射试验,测量了弹射过程中的内弹道压力参数,结合试验开展情况讨论了该发射系统的内弹道特点,提出了空气发射系统中管路及阀门应注意的事项。将仿真计算的结果与试验测试数据进行对比分析,结果表明计算结果与试验结果吻合较好,满足多级杆式空气发射系统的研制需要。所建立的内弹道模型可指导特定发射需求气瓶初始压力及开阀控制时序的参数制定,对某多级杆式空气发射系统的研制具有参考意义。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [16] |
潘霄, 姜毅, 王博漫, 等. 火箭多级筒燃气弹射动力学特性及影响因素[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(6):1277-1287.
为提高火箭弹射的性能,研究一种新型改进火箭多级筒燃气弹射装置的安全性,对其弹射过程中结构的动力学特性及发射过程中的影响因素进行比较分析。使用有限元方法对该弹射装置的弹射过程进行仿真,将弹射出的火箭位移、速度、俯仰角等结果与实验结果进行对比,验证有限元计算模型的有效性。在有限元模型基础上分析筒节间隙、推力偏心和发射角度对多级筒弹射安全性的影响。分析结果表明:发射角度是弹射安全性的主要影响因素,筒节间隙和推力偏心是次要影响因素,火箭弹射偏转、筒节间相互作用力和横向最大位移增大都是这些因素影响弹射安全性的主要表现;当活塞筒筒节间隙扩大到0.3 mm或发射角度偏转到3°时,会对发射安全性产生较大的威胁。
The dynamic characteristics of a multistage canister gas ejection structure and the influencing factors during ejection are analyzed to improve the ejection performance of rockets and to study the safety of gas ejection structure. The structural composition,topological relationship and excitation load of the rocket multistage canister ejection system are analyzed,and a finite element model of the ejection system are established for simulation analysis. Through experiments,it is verified that the simulation accuracy of finite element model meets the simulation requirements. The influences of the gap of cylinder section,the thrust eccentricity and the launch angle on the safety of multistage canister gas ejection structure are analyzed based on the finite element model. It's found that the launch angle is the main influencing factor that affects the ejection safety,and the gap between the cylinder sections and the thrust eccentricity have also effect on the ejection safety. he influencing factors lead to the ejection deflection of rocket,the interaction force between the canister sections and the increase in the maximum lateral displacement. When the gap between the canister sections is increased to 0.3 mm or the launch angle is deflected to 3°,a greater threat will be posed to ejection safety.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [17] |
王璟慧, 姜毅, 杨昌志, 等. 模块燃气压强差异对多级杆弹射影响[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2022, 42(3):78-84.
针对多模块多级活塞杆冷弹射过程中燃气压强差异导致的弹射模块不同步问题,研究模块同步性对弹射装置性能和火箭动力学响应的影响。建立数学模型推导分析多级活塞杆模块运动同步性与动力同步性的关系;搭建三模块八级活塞杆动力学模型,考虑燃气压强差异导致的动力不同步,研究弹射装置的运动同步性、结构安全性和火箭的动力学响应。结果表明:由于实际火箭质量约为动力模块质量的20倍,满足运动同步性的质量条件,火箭与弹射模块总是保持运动同步性;缓冲装置压缩变形量累积使得各模块有效行程不同,弹射时长不同;三模块动力同步性差异越大对弹射装置安全性与火箭离轨姿态越不利,多级活塞杆最大应力增大,火箭的离轨时间增加,离轨时刻的俯仰角速度和偏航角速度增大。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [18] |
任锐, 马大为, 姚琳, 等. 多级气动液压弹射装置建模及性能研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(8):1365-1372.
分析气动液压弹射方式的两种弹射装置类型,研究一种以压缩空气为动力源、油液为传动介质,且具备油液自缓冲结构的多级气动液压弹射装置的弹射性能。针对弹射过程中气腔气体复杂多变过程、封闭油腔油液流动非线性、多级缸运动关系的不确定性及油液缓冲结构,结合真实气体热力学效应,推导封闭油腔油液的压力动态变化模型及多级缸动力学非线性模型,建立描述多级气动液压弹射过程的数学模型;通过数值求解方法,分析该多级气动液压弹射缸的运动规律及弹射性能。研究结果表明:该多级气动液压弹射缸建压过程迅速,并能在0.2 s内以2.4 m有效弹射行程,将重1.5 t负载加速至19 m/s,弹射最大过载不超过16 g,且相邻两级缸的相对速度不超过15 m/s. 分析气动液压弹射方式的两种弹射装置类型,研究一种以压缩空气为动力源、油液为传动介质,且具备油液自缓冲结构的多级气动液压弹射装置的弹射性能。针对弹射过程中气腔气体复杂多变过程、封闭油腔油液流动非线性、多级缸运动关系的不确定性及油液缓冲结构,结合真实气体热力学效应,推导封闭油腔油液的压力动态变化模型及多级缸动力学非线性模型,建立描述多级气动液压弹射过程的数学模型;通过数值求解方法,分析该多级气动液压弹射缸的运动规律及弹射性能。研究结果表明:该多级气动液压弹射缸建压过程迅速,并能在0.2 s内以2.4 m有效弹射行程,将重1.5 t负载加速至19 m/s,弹射最大过载不超过16 g,且相邻两级缸的相对速度不超过15 m/s.
A novel multi-stage pneumatic and hydraulic catapult device with oil buffering structure,which utilizes compressed air as impetus and hydraulic fluid as transmission medium, is introduced and its ejection performance is researched by analyzing two typical catapult devices involving pneumatic and hydraulic catapult. According to the complex polytropic process of gas, the flow nonlinearity of hydraulic fluid in enclosed chamber, motion uncertainty of multi-stage cylinders and the self-buffering structure, a mathematical model describing multi-stage pneumatic and hydraulic catapult process is established based on real gas thermodynamic effect. Meanwhile, the dynamic variation model of oil pressure in enclosed chamber and the nonlinear dynamic model of multi-stage cylinders are constructed. The motion laws and working performance of multi-stage pneumatic and hydraulic catapult cylinder are obtained through numerical simulation. The results show that the proposed multi-stage pneumatic and hydraulic catapult device can generate the appropriate pressure quickly and accelerate the load up to 19 m/s within 0.2 s with the speed-up distance of 2.4 m, and thus the overload is less than 16 g and the relative velocity between two adjacent cylinders is less than 15 m/s.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [19] |
王雪琴, 马吴宁, 马大为, 等. 考虑泄露的无杆式高压气动弹射器内弹道精确建模就试验[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(7):1867-1880.
无杆式高压气动弹射器因开口的固有结构决定其存在一定量的泄漏,为此设计并开展样机泄漏测试试验。基于由实验数据拟合的标准干空气热力学状态方程,分别按理想气体和真实气体对比计算泄漏率,并拟合泄漏率随压力、行程变化的经验公式。建立考虑动态泄漏、真实气体效应及真实开阀规律的精确内弹道模型,对考虑和不考虑泄漏两种工况的结果进行对比,并详细分析考虑泄漏的弹射过程中热力学参数与负载运动参数的变化规律,将其与弹射试验数据、流体仿真结果进行对比。研究结果表明:按理想气体计算的泄漏率比真实气体偏小约4%;泄漏率不超过4%/s;考虑泄漏的精确内弹道模型计算结果与弹射试验数据、流体仿真结果均基本一致,具有较高的计算精度。
The rodless high-pressure pneumatic catapult experiences a certain amount of leakage due to the inherent structure of the opening. In this study, a prototype leakage test is designed and conducted. Based on the standard dry air thermodynamic equation of state fitted by the experimental data, the leakage rate is calculated and compared under the hypothesis of ideal gas and real gas. The empirical formula of leakage rate varying with pressure and stroke is fitted. An accurate interior ballistic model considering dynamic leakage, real gas effects, and the real valve opening law is established. The two working conditions with and without leakage are solved numerically and compared. Then, the variation laws of thermodynamic parameters and load motion parameters in the ejection process with leakage are analyzed in detail and compared with the ejection test data and fluid simulation results. The results show that the leakage rate calculated under ideal gas assumption is about 4% lower than that under real gas assumption. Moreover, the calculated leakage rate shall not exceed 4%/s. The calculation results of the accurate interior ballistic model considering leakage are basically consistent with the ejection test data and the fluid simulation results, indicating high calculation accuracy. {{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [20] |
姚琳, 马大为, 人杰, 等. 高速无杆气缸作动器密封圈润滑性能分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2017, 51(8):1568-1574.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [21] |
闫晴宵, 李鹏永, 常书丽. 钢丝绳气缸式弹射装置陆上及水下弹射内弹道对比分析[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2018, 40(8):141-143.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
陈宗杨, 练永庆, 李昂. 下钢缆拖拽弹射鱼雷内弹道仿真[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2022, 30(2):209-215.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [23] |
孟艳, 王玺, 郭锦炎, 等. 多级活塞缸式弹射装置结构安全性分析[J]. 弹道学报, 2020, 32(2):56-61.
多级活塞缸式发射装置作为新型冷发射方式之一,具有兼容不同弹径、免装填等优点。为研究多级活塞缸式发射装置的结构安全性,通过理论分析、数值仿真等方法对多级活塞缸式发射装置的运动过程进行了梳理,分析了多级活塞缸式发射装置中缓冲材料的吸能需求,并揭示了结构质量特性偏差、装配姿态偏差、燃气动力偏差、缓冲材料特性偏差等因素对导弹离台姿态的影响规律。多级活塞缸式发射装置的运动规律由各级缸筒的几何参数和被推动导弹的质量参数决定,对缓冲吸能的需求较高,多模块的多级活塞缸式发射装置中导弹的离台姿态更加稳定。研究结果可为多级活塞缸式发射装置安全性设计提供理论支撑,为多级活塞缸式发射武器系统提供指标分解依据。
As one of the new cold launching methods,the multi-stage piston cylinder launching equipment has the advantages of compatibility with different sizes of missile and loading free. In order to analyze structure safety of multi-stage piston cylinder launching equipment,the kinematic mechanism of the multi-stage piston cylinder launching equipment was studied by theoretical analysis and numerical simulation method,and the critical demands in energy absorbing of multi-stage piston cylinders were established. Influences of mass properties deviation,assembly posture deviation,gas power deviation,and cushioning material deviation on the attitude of missile were studied. The kinematic mechanism of the multi-stage piston cylinder launching equipment is determined by the geometry of the cylinder and the mass properties of the propelled missile. There is a high demand of energy absorbing in multi-stage piston cylinders. The off-platform attitude of missile is more stable in multi-module multi-stage piston cylinder launching equipment. The results can provide theoretical support for safety design of multi-stage piston cylinder launching equipment structure and weapon system index decomposition.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [24] |
冯江涛, 高钦和, 管文良, 等. 多级液压缸建模及级间缓冲研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(12):2268-2276.
大型起竖装置普遍采用多级液压缸驱动,在缸体初始长度相同的情况下,多级缸较单级缸行程更长,但是其结构也更复杂。为得到多级缸的特性,基于容腔节点法建立了多级缸的运动模型,考虑润滑油膜的信息改进了LuGre摩擦力模型,采用迟滞因子的等效阻尼模型改进了接触力模型,完成了多级缸驱动起竖过程的仿真。多级缸换级时作用面积突变,导致压力和速度突变,产生过大的冲击,为减小换级冲击,在缸筒上布置多个缓冲小孔。仿真结果表明:采用缓冲结构后,换级时缸筒同步运动,将压力突变转化为缓变,提前将压力增大至下一级缸筒工作压力,大幅度减小了换级时的速度和加速度波动。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [25] |
周文平, 杨杉. 多级液压缸级间缓冲性能数值模拟[J]. 机床与液压, 2021(12):171-174.
多级液压缸换级时的级间缓冲性能会对液压系统工作的平稳性及安全性产生影响。以某三级液压缸为例,采用基于动网格及UDF (用户自定义函数)的三维非稳态计算流体力学方法,并计入活塞与缸筒的摩擦力,对收回阶段的液压油流动及活塞运动特性进行计算,分析液压缸的缓冲和换级性能。结果表明:采用圆柱形缝隙节流效果明显,但单个活塞收回时间较长,存在两级活塞同时运动的情况;换级时会产生较大的压力及加速度突变,导致系统产生液压冲击和振动。模拟结果能够为多级液压缸缓冲结构的优化设计提供参考。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [26] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [27] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [28] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [29] |
何小英, 彭雪明, 王惠军. 基于多燃气动力的水下变深度发射内弹道[J]. 弹道学报, 2019, 31(2):14-18.
为研究水下变深度发射导弹的内弹道问题,通过由多个燃气发生器组成的弹射动力系统,建立了水下发射的内弹道计算模型,介绍了可同时满足多种深度发射的内弹道仿真方法,进行了仿真计算。结果表明:在20~60 m的深度范围发射,可以通过调节3个燃气发生器的点火时序,得到18.9 m/s±3.4 m/s的出筒速度调节范围。由多燃气发生器组成的弹射动力系统是解决变深度发射导弹的有效途径。
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(10539 KB)
PDF(10539 KB)
Collection(s)
 Fig.1 The working principle diagram of ejection device
Fig.1 The working principle diagram of ejection device Fig.2 Schematic diagram of throttle hole buffering
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of throttle hole buffering Fig.3 Schematic diagram of water flow in piston cylinder
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of water flow in piston cylinder Fig.4 Schematic diagram of forces on a torpedo
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of forces on a torpedo Fig.5 Schematic diagram of data exchange
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of data exchange Table 1 The parameters of ejection device
Table 1 The parameters of ejection device Table 2 Initial values of input variables
Table 2 Initial values of input variables Fig.6 Pressure p2 in reverse cavity of piston cylinder in different drainage hole schemes
Fig.6 Pressure p2 in reverse cavity of piston cylinder in different drainage hole schemes Fig.7 Velocity vw of water flow in different drainage hole schemes
Fig.7 Velocity vw of water flow in different drainage hole schemes Fig.8 Acceleration ap of piston in different drainage hole schemes
Fig.8 Acceleration ap of piston in different drainage hole schemes Fig.9 Velocity vp of piston in different drainage hole schemes
Fig.9 Velocity vp of piston in different drainage hole schemes Fig.10 Displacement xp of piston in different drainage hole schemes
Fig.10 Displacement xp of piston in different drainage hole schemes Fig.11 Velocity vp of piston under different ambient pressures
Fig.11 Velocity vp of piston under different ambient pressures Fig.12 Displacement xp of piston under different ambient pressures
Fig.12 Displacement xp of piston under different ambient pressures Fig.13 Velocity vt curves of torpedo under different ambient pressures
Fig.13 Velocity vt curves of torpedo under different ambient pressures Fig.14 The rate of pitch angle ω of torpedo under different ambient pressures
Fig.14 The rate of pitch angle ω of torpedo under different ambient pressures Fig.15 Displacement ya of torpedo tail under different ambient pressures
Fig.15 Displacement ya of torpedo tail under different ambient pressures Fig.16 Schematic diagram of ejection device
Fig.16 Schematic diagram of ejection device Fig.17 Schematic diagram of principle experiment in high pressure water tank laboratory
Fig.17 Schematic diagram of principle experiment in high pressure water tank laboratory Fig.18 The picture of principle test ejection device
Fig.18 The picture of principle test ejection device Fig.19 Pressure curve of piston cylinder
Fig.19 Pressure curve of piston cylinder Fig.20 Acceleration at of torpedo
Fig.20 Acceleration at of torpedo Fig.21 Velocity vt of torpedo
Fig.21 Velocity vt of torpedo Fig.22 Displacement curves
Fig.22 Displacement curves Fig.23 Acceleration at of torpedo in different ejection schemes
Fig.23 Acceleration at of torpedo in different ejection schemes Fig.24 Velocity vt of torpedo in different ejection schemes
Fig.24 Velocity vt of torpedo in different ejection schemes Fig.25 Pressure curves of piston cylinder in different ejection schemes
Fig.25 Pressure curves of piston cylinder in different ejection schemes Fig.26 Pressure curves of piston cylinders with different working media
Fig.26 Pressure curves of piston cylinders with different working media Fig.27 Acceleration at of torpedos with different working media
Fig.27 Acceleration at of torpedos with different working media Fig.28 Velocity vt of torpedos with different working media
Fig.28 Velocity vt of torpedos with different working media/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |